Grid refinement
In yt, you can now generate very simple initial conditions:
In[1]:
from yt.mods import *
from yt.frontends.stream.api import load_uniform_grid
from yt.frontends.gdf.api import *
from yt.utilities.grid_data_format.writer import write_to_gdf
class DataModifier(object):
pass
class TophatSphere(DataModifier):
def __init__(self, fields, radius, center):
self.fields = fields
self.radius = radius
self.center = center
def apply(self, grid, container):
r = ((grid['x'] - self.center[0])**2.0
+ (grid['y'] - self.center[1])**2.0
+ (grid['z'] - self.center[2])**2.0)**0.5
for field in self.fields:
grid[field][r < self.radius] = self.fields[field]
data = na.random.random((256, 256, 256))
ug = load_uniform_grid({'Density': data}, [256, 256, 256], 1.0)
spheres = []
spheres.append(TophatSphere({"Density": 2.0}, 0.1, [0.2,0.3,0.4]))
spheres.append(TophatSphere({"Density": 20.0}, 0.05, [0.7,0.4,0.75]))
for sp in spheres: sp.apply(ug.h.grids[0], ug)
p = ProjectionPlot(ug, "x", "Density")
p.show()
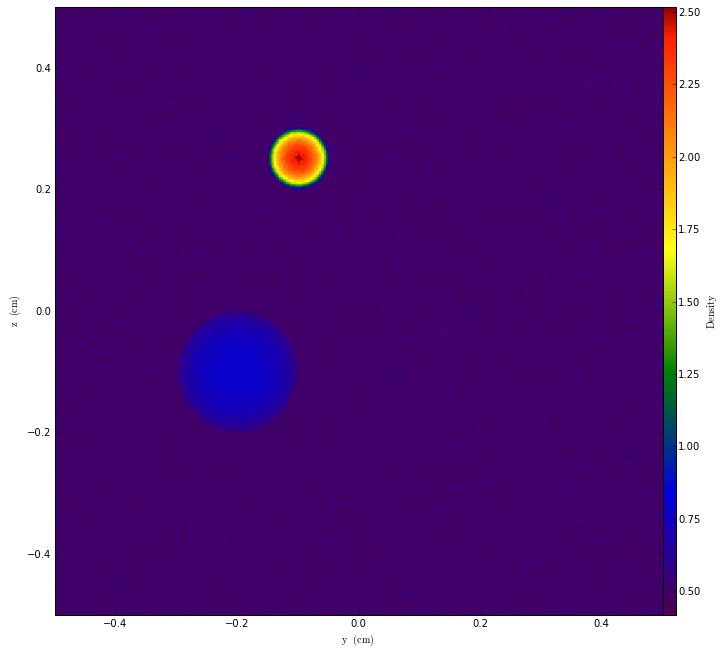
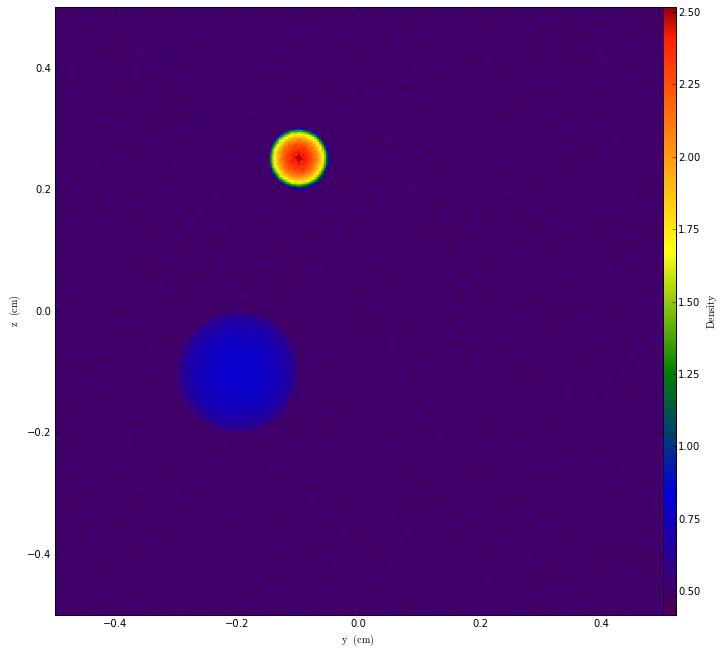
We can even save them out to disk!
write_to_gdf(ug, "/home/mturk/test.gdf")
pf = GDFStaticOutput("/home/mturk/test.gdf")
p2 = ProjectionPlot(pf, "x", "Density")
p2.show()
Over time, this functionality will expand to include cell-flagging, refinement, and much more interesting modifications to grid values.