Jupyter Notebook Access
Table of contents
Requirements
- Compile
libytin jupyter kernel mode. - Call libyt API
yt_run_JupyterKernel. - Python package
jupyter_libyt,jupyter-client, andjedi.
Setting Up
During simulation runtime, libyt will activate libyt Jupyter kernel. We need another process to start Jupyter Notebook/JupyterLab and connect to libyt Jupyter kernel.
Starting Jupyter Notebook / JupyterLab
The process of starting Jupyter Notebook/JupyterLab and running simulation are separate and independent.
- Get
jupyter_libytandjupyter-client. - After installing
libyt, add<libyt-install-dir>/share/jupytertoJUPYTER_PATH.export JUPYTER_PATH=<libyt-install-dir>/share/jupyter:$JUPYTER_PATHCheck if
libyt_kernelis listed:jupyter kernelspec list - Export environment variable
LIBYT_KERNEL_INFO_DIRto where the simulation executable directory is.export LIBYT_KERNEL_INFO_DIR=<path-to-simulation-dir> - Launch Jupyter Notebook/JupyterLab
jupyter notebook jupyter-lab - Click
Libytto connect to libyt Jupyter kernel once the libyt Jupyter kernel is activated.
Running Simulation
- Compile
libytin jupyter kernel mode. - Call libyt API
yt_run_JupyterKernel. When flag file is detected,libytwill activate libyt Jupyter kernel. - libyt API
yt_run_JupyterKernelreturnsYT_SUCCESSafter libyt Jupyter kernel shuts down (see How to Exit). - Simulation can continue its process.
Example
Using Jupyter Notebook / JupyterLab
Basics
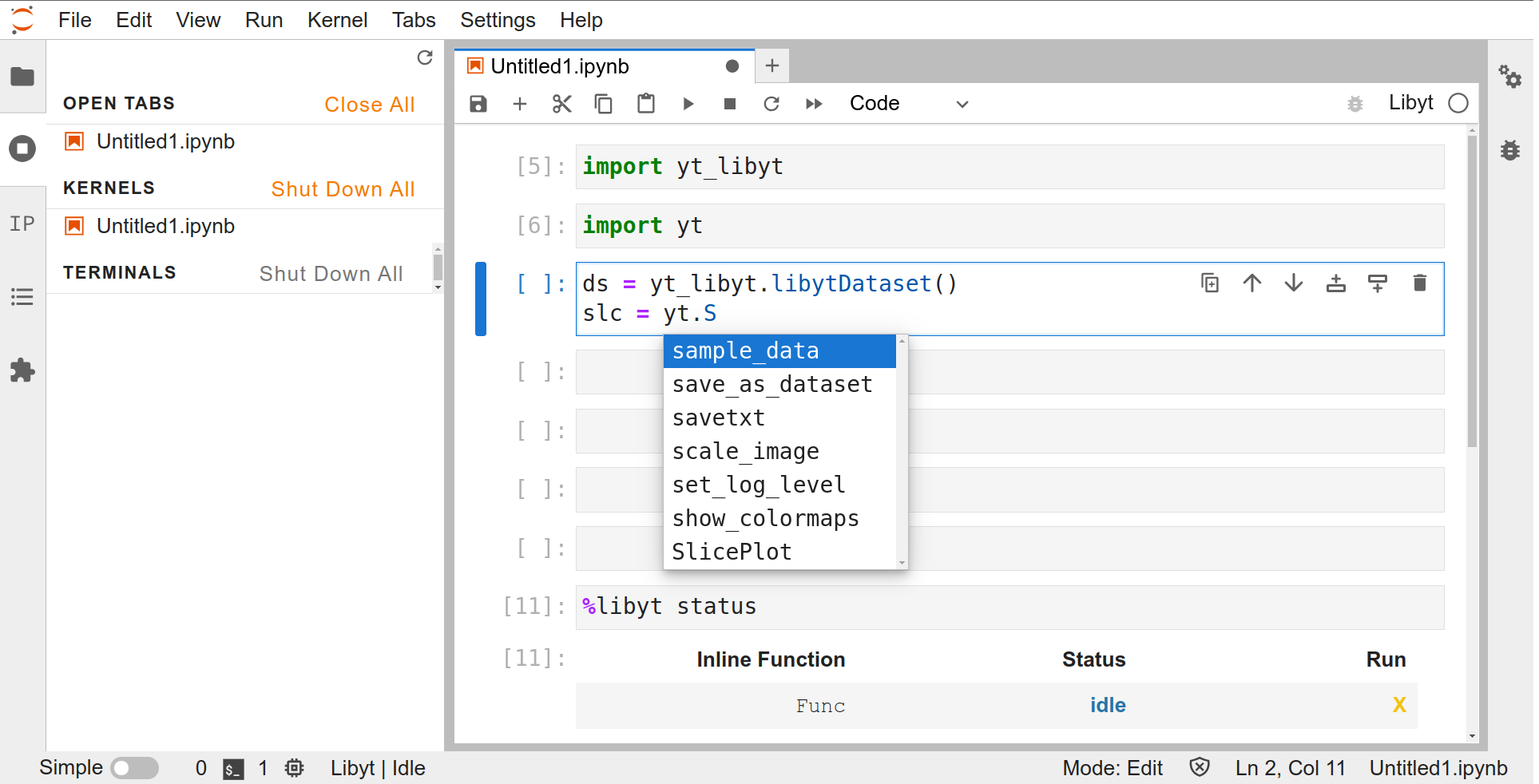
Python Prompt and libyt Defined Commands
The cell takes Python statements and libyt Defined Commands. It can also import other Python modules
How does it execute Python statements and libyt defined commands?
- Takes user inputs in the cell.
- MPI root process broadcasts the inputs to other processes.
- Every other MPI process executes the same piece of input synchronously.
- Get outputs from each process and print feedbacks on the screen.
Changes is kept and maintain in user’s inline script’s namespace in situ analysis in the following round.
Auto-Completion
Use TAB key to do auto-completion.

jedimust be installed to use this feature. Generally, if you haveIPythoninstalled, you probably already havejedi.
User Interface
This is traditional Jupyter Notebook UI.
If the notebook is connected to libyt Jupyter kernel, restarting only exits the kernel, and libyt API
yt_run_JupyterKernelreturns. It won’t restart another kernel.
How to Exit
Go to “Running Terminals and Kernels” -> “Shutdown Kernel”.
“Interrupt the kernel” button (![]() ) won’t have any effect.
) won’t have any effect.
Reconnecting to libyt Jupyter Kernel
After exiting the kernel and returning to simulation process, we don’t need to close the entire notebook to reconnect to the new libyt Jupyter kernel launched by the following step. We can press “Restart” button (![]() ) to reconnect to libyt Jupyter kernel.
) to reconnect to libyt Jupyter kernel.
Make sure you already disconnect libyt Jupyter kernel before reconnecting. Otherwise, libyt Jupyter kernel will simply shutdown the kernel. There will be a pop-up window asking “if you want to restart” if you are already connected to a libyt kernel.
Known Limitations
- The functionality is limited to taking Python inputs and printing outputs from all the MPI processes only.
libythasn’t done implementing Jupyter’s full feature, like data streaming, supportingipwidgetsyet. - See Limitations in MPI Related Python Tasks.